DARPA Seeks to Improve 5G Network Security
DARPA has announced a new program that seeks to leverage open source software and systems to address security challenges facing 5G and future wireless networks.
Emerging 5G mobile wireless networking technologies are slated to dramatically increase in both scale and speed, enabling much faster access to data collected from billions of connected devices. This new flexibility offers many benefits, but at the same time introduces novel security challenges. Today’s proprietary 5G technologies make it difficult to achieve the transparency necessary for security-related risk analysis and mitigation.
“As networks are simultaneously critical infrastructure and the means used for cyberespionage and cyberwarfare, finding ways to bolster their security is critically important,” said DARPA program manager, Dr. Jonathan Smith. “The rapid increase in the scale of 5G networks, as well as issues from unmanaged or forgotten Internet of Things (IoT) devices and unwanted interactions between network slices, create security risks that must be addressed.”
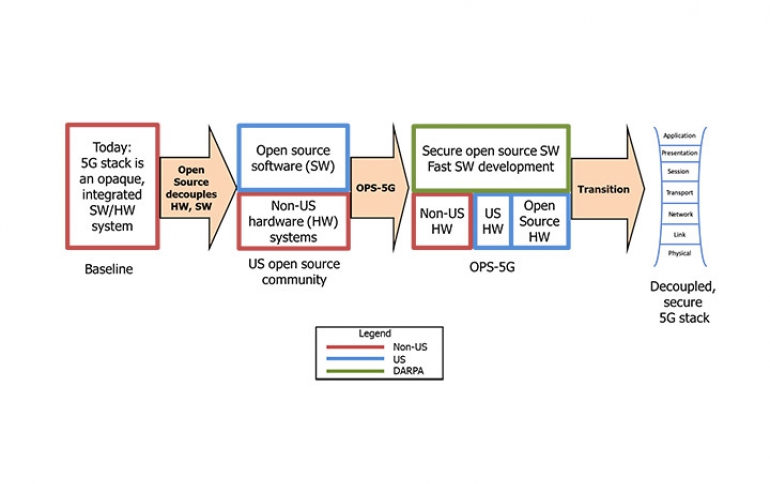
DARPA created the Open, Programmable, Secure 5G (OPS-5G) program to tackle many of the security challenges facing future wireless networks. OPS-5G will explore the development of a portable, standards-compliant network stack for 5G mobile networks that is open source, and secure by design. The program seeks to enable a “plug-and-play” approach to various network software and hardware components, which reduces reliance on untrusted technology sources. The goal of OPS-5G is to develop open source software and systems that can enable more secure 5G as well as future generations of networks beyond 5G.
The signature security advantage of open source (OS) software is increased code visibility, meaning that code can be examined, analyzed, and audited manually and, more fruitfully, with automated tools by multiple parties. Another benefit is open source software’s portability, which allows the software to run on both OS and proprietary hardware. This decoupling of the hardware and software ecosystems makes it easier to introduce innovations while raising the difficulty of some malicious attacks. Further, it helps open the 5G market to smaller players and innovators. However, creating open source software elements typically requires the collaborative development of well-defined standards. The standards creation process can be slow and arduous – one that a rapidly-progressing technology such as 5G can’t afford. To help accelerate the development of 5G-relevant open source software from standards, OPS-5G will explore the use of machine translation to increase code development velocity and help make standards easier to understand.
One of the many benefits of 5G is powering a vast and growing ecosystem of IoT devices. The security across these devices, however, is disparate, as is their size, weight, and power (SWaP). Today, IoT security features are viewed as optional, which does not bode well for their use within defense systems. To bolster security around this growing mesh of technologies, OPS-5G will explore the development of cost-effective SWaP-conscious cryptography with scalable security protocols. The program will look to existing technologies to support this process, like the many-to-many end-to-end encryption protocol developed by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, called Joining Encryption and Delegation for IoT.
Network elements used to support virtualization and the 5G network concept of application-customized “slices” share resources to achieve cost-effective performance. Amongst other risks, this resource sharing creates potential timing channel vulnerabilities. Opaque system ownership, operator policies, and software provenance also present security issues for 5G networks. Currently, a multitude of large vendors provide carrier hardware, software, node provisioning, and more to enable 5G technologies. OPS-5G will explore breakthrough approaches for the enablement of secure network slices to provide security across the network resources provided by and shared with unknown entities. The program will explore novel ways to make trusted networks out of infrastructures with untrusted components.
Finally, OPS-5G will aim to address security challenges posed by 5G’s programmability by hardening the execution. 5G is expected to have 60-600 billion nodes by 2023, which radically increases the risk of network attack. To increase network resiliency and enable faster adaptation to threats, OPS-5G will explore the development of programmable elements of 5G specifically for defense.
Additional information is available here.





















