1. About the Intel Core i7 series

Intel had announced the new i7 core series a long time ago. The new series of processors feature some interesting improvements over the previous C2D series. The most noticeable change is the new LGA 1366 socket that the Core i7 uses, meaning that it works in a new motherboard, as well as the support for triple DDR3 memory. All the latest Nehalem processors come with a 8MB L2 cache and the FSB has been replaced by the Intel QuickPath Interconnect architecture, which achieves data transfer speeds as high as 25.6 GB/s. Besides these obvious changes, Intel the Core i7 series are considered as the company's first "real" Quad core processor incorporating multiple cores on a single processor die.
Moreover, the Core i7 processors eliminate the need for the Northbridge chipset to manage system memory and link it to the processor with an integrated, on-die memory controller which links the processor directly to the system memory. This is what AMD Phenom series have been using for sometime now, so we are excited to see Intel improving the way it manages the available memory resources, which will hopefully lead to a better performance. More information for the Core i7 is available at the Intel' s white paper.
Below you can see a summary of the important features of the Core i7 processors.
| Feature |
Benefit |
| Quad Core Processing |
Provides four independent execution cores in one processor package. Four dedicated processing cores help operating systems and applications deliver additional performance, so end users can experience better multitasking and multithreaded performance across many types of applications and workloads. |
| Intel Hyper-Threading Technology |
Delivers two processing threads per physical core for a total of eight threads for massive computational throughput. With Intel Hyper-Threading Technology, highly threaded applications can get more work done in parallel, completing tasks sooner. With more threads available to the operating system, multitasking becomes even easier. This amazing processor can handle multiple applications working simultaneously, allowing you to do more with less wait time. |
| Intel Turbo Boost Technology |
Dynamically increases the processor's frequency as needed by taking advantage of thermal and power head-room when operating below specified limits. Get more performance automatically, when you need it the most. |
| 8 MB IntelSmart Cache |
Dynamically increases the processor's frequency as needed by taking advantage of thermal and power head-room when operating below specified limits. Get more performance automatically, when you need it the most. |
| Intel QuickPath Interconnect |
Intel's latest system interconnect design increases bandwidth and lowers latency, while achieving data transfer speeds as high as 25.6 GB/s. |
| Integrated Memory Controller |
An integrated memory controller with three channels of DDR3 1066 MHz offers memory performance up to 25.6 GB/s. Combined with the processor's efficient prefetching algorithms, this memory controller's lower latency and higher memory bandwidth delivers amazing performance for data-intensive applications. |
| IntelHD Boost |
Includes the full SSE4 instruction set, significantly improving a broad range of multimedia and compute-intensive applications. The 128-bit SSE instructions are issued at a throughput rate of one per clock cycle allowing a new level of processing efficiency with SSE4-optimized applications. |
| Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) |
Provides for more efficient processor and platform thermal control improving system acoustics. The DTS continuously measures the temperature at each processing core. The ability to continuously measure and detect variations in processor temperature enables system fans to spin only as fast as needed to cool the system. The combination of these technologies can result in significantly lower noise emissions from the PC. |
| IntelWide Dynamic Execution |
Improves execution speed and efficiency, delivering more instructions per clock cycle. Each core can complete up to four full instructions simultaneously. |
| IntelSmart Memory Access |
Improves system performance by optimizing the use of the available data bandwidth from the memory subsystem and reducing the effective latency of memory accesses. |
The Core i7 series of CPUs include three models.  retail price. The i7-965 features a higher clock speed and a faster QuickPath Interconnect that further boosts performance. Looking at the retail price, the lower-end i7-920 CPU is an interesting solution priced at $289, while the i7-940 rumps up to $540 and the highest-end i7-965 up to $999. While the i7-965 is very expensive, it has two features that overclockers will love: the overspeed protection has been removed and there is not any multiplier lock. The TDP is at 130 Watts - which is still high for a Quad core CPU- but the 45nm design should be able to deliver high speeds without requiring the use of huge CPU coolers.
retail price. The i7-965 features a higher clock speed and a faster QuickPath Interconnect that further boosts performance. Looking at the retail price, the lower-end i7-920 CPU is an interesting solution priced at $289, while the i7-940 rumps up to $540 and the highest-end i7-965 up to $999. While the i7-965 is very expensive, it has two features that overclockers will love: the overspeed protection has been removed and there is not any multiplier lock. The TDP is at 130 Watts - which is still high for a Quad core CPU- but the 45nm design should be able to deliver high speeds without requiring the use of huge CPU coolers.
Processor
Number |
Cores/Threads |
Clock Speed |
Intel QuickPath Interconnect |
Intel Smart Cache |
Silicon |
Turbo Boost |
i7-965 |
4 / 8 |
3.0 GHz |
6.4 GT/sec |
8 MB |
45 nm |
Up to 3.46 GHz Boost |
i7-940 |
4 / 8 |
2.93 GHz |
4.8 GT/sec |
8 MB |
45 nm |
Up to 3.46 GHz Boost |
i7-920 |
4/ 8 |
2.66 GHz |
4.8 GT/sec |
8 MB |
45 nm |
Up to 3.46 GHz Boost |
An additional feature of the new CPUs is the Turbo Boost that adds more performance to your system. This gain is noticeable in cases where an application actually uses all four cores of the processor. The CPU-Z software will report some additional 133Mhz to the running speed of the CPU when the Turbo Boost is enabled. Of course, it can be turned off from the motherboard BIOS.
We should also mention here that the Core i7 processors are working together with a motherboard based on the new X58 chipset.
More information on the Intel i7-920 series is available over Intel's web site.
2. Package, installation
The Intel Core i7-920 costs around €285 as found at several online stores around Europe. The blue retail package is easily recognizable from the new Core i7 logo and its much bigger volume compared to the C2D series:



The included cpu cooler looks bigger than what we have seen with 45nm Quad core series.



- Installation
Installing the PCU in the new LGA 1366 socket is not any different than what you may have already experienced with the previous LGA 775 processors. The socket's design does not allow you to install the CPU in a wrong way:


Push the CPU bracket down until you here the click locking sound.
Your new Core i7 processor should be ready to go in just three minutes.


After connecting all necessary power cables, you can power up your system. Using the latest CPU-Z we can see more details about the installed processor:


The default core voltage of the Core i7 series is 1.10V, with a maximum of 1.45V. For our tests we used the Foxconn Renaissance X58 motherboard with the bios Ver. P07 installed.

The memory we used is the Crucial DDR3-1066 rated at CL7-7-7-20-1T with 1.55V. According to Intel, the memory voltage should not exceed the 1.65V in order to avoid damaging the CPU.


Below is the testbed configuration we used in this test:
- CPU Cooler: Intel Core i7
- Motherboard: Foxconn Resaissance P07 bios
- Memory: 3x1GB Crucial DDR3-1066 (533 @ 7-7-7-20-1T, 1.50V)
- VGA: MSI 7600GT Silent with latest Nvidia drivers installed
- HDD: WD 80GB SATA (primary)
- HDD: WD 80GB SATA (secondary)
- Operating system: Windows XP SP2 with all latest updates installed
- Operating system: Windows VISTA 32bit SP1 with all latest updates installed
Benchmark software
- Office/Benchmarks (WinXP)
- Sisoft Sandra 2008 SP2
- Everest Lavasys Ultimated Edition 2007 v4.50
- SuperPI Mod v1.5XS
- wPrime v1.55 (stable)
- Cinebench vR10
- x264 Benchmark
- x264 HD Benchmark
- SysMark 2007 Preview
- TMPGEnc 4.0 Xpress
- Gaming/Benchmarks (VISTA 32bit)
- PC Mark Vantage v1.00 Nov Edition
- 3D Mark06 v1.2.0
- Crysis Retail v1.20
3. Benchmarks - Everest Ultimate Edition, SiSoftware Sandra
- Everest Ultimate Edition
 EVEREST Ultimate Edition is a leading system diagnostics and benchmarking solution for enthusiasts PC users, based on the EVEREST Technology. During system optimizations and tweaking it provides essential system and overclock information, advanced hardware monitoring and diagnostics capabilities to check the effects of the applied settings. CPU, FPU and memory benchmarks are available to measure the actual system performance and compare it to previous states or other systems. Furthermore, complete software, operating system and security information makes EVEREST Ultimate Edition a comprehensive system diagnostics tool that offers a total of 100 pages of information about your PC. The software has build-in several tests for memory and CPU/FPU.
EVEREST Ultimate Edition is a leading system diagnostics and benchmarking solution for enthusiasts PC users, based on the EVEREST Technology. During system optimizations and tweaking it provides essential system and overclock information, advanced hardware monitoring and diagnostics capabilities to check the effects of the applied settings. CPU, FPU and memory benchmarks are available to measure the actual system performance and compare it to previous states or other systems. Furthermore, complete software, operating system and security information makes EVEREST Ultimate Edition a comprehensive system diagnostics tool that offers a total of 100 pages of information about your PC. The software has build-in several tests for memory and CPU/FPU.

The triple-channel DDR3 memory used on the Core i7/X58 platform seems to make the difference here, especially at the memory tests. Compared to the Intel C2D/C2Q series as well as the AMD 9950 BE CPU, the i7-920 seems to be 25-30% faster in the memory tests.
The performance we got in the CPU and FPU tests is also much better than you can get from any previous AMD/Intel platform.


 SiSoftware Sandra (the System ANalyser, Diagnostic and Reporting Assistant) is an information & diagnostic utility. It should provide most of the information (including undocumented) you need to know about your hardware, software and other devices whether hardware or software. It works along the lines of other Windows utilities, however it tries to go beyond them and show you more of what's really going on. Giving the user the ability to draw comparisons at both a high and low-level. You can get information about the CPU, chipset, video adapter, ports, printers, sound card, memory, network, Windows internals, AGP, PCI, PCIe, ODBC Connections, USB2, 1394/Firewire, etc. Sisoft Sandra offers a variety of tests for Memory and CPU.
SiSoftware Sandra (the System ANalyser, Diagnostic and Reporting Assistant) is an information & diagnostic utility. It should provide most of the information (including undocumented) you need to know about your hardware, software and other devices whether hardware or software. It works along the lines of other Windows utilities, however it tries to go beyond them and show you more of what's really going on. Giving the user the ability to draw comparisons at both a high and low-level. You can get information about the CPU, chipset, video adapter, ports, printers, sound card, memory, network, Windows internals, AGP, PCI, PCIe, ODBC Connections, USB2, 1394/Firewire, etc. Sisoft Sandra offers a variety of tests for Memory and CPU.



The Sisoft Sandra tests confirmed that the Intel i7-920 processor is much faster than any other processor we have tested in past.
We should apologize here for some strange results that appear in the graphs in some tests. The specific test results are coming from our database and were conducted with a previous version of the Sisoft Sandra software.
4. Benchmarks - PCMark Vantage, SYSmark 2007 Preview
 PCMark Vantage is the first objective hardware performance benchmark for PCs running 32 and 64 bit versions of Microsoft Windows Vista. PCMark Vantage is suited for benchmarking any type of Microsoft Windows Vista PC from multimedia home entertainment systems and laptops to dedicated workstations and hi-end gaming rigs. The software shows the user where their system soars or falls flat, and how to get the most performance possible out of their hardware.
PCMark Vantage is the first objective hardware performance benchmark for PCs running 32 and 64 bit versions of Microsoft Windows Vista. PCMark Vantage is suited for benchmarking any type of Microsoft Windows Vista PC from multimedia home entertainment systems and laptops to dedicated workstations and hi-end gaming rigs. The software shows the user where their system soars or falls flat, and how to get the most performance possible out of their hardware.

The PCMark Vantage is mainly based on 2D applications, which do not benefit from the multi-core CPUs. As a result, the higher clock of the Intel E8600 CPU was more efficient here but only in the productivity, communications and music tests. The Intel i7-920 CPU showed its teeth in the Gaming, TV&Movies and Memories tests, where the processor was significantly better than the rest CPUs by Intel and AMD.
 BAPCo's SYSmark 2007 Preview is an application-based benchmark that reflects
usage patterns of business users in the areas of Video creation,
E-learning, 3D Modeling and Office Productivity.
BAPCo's SYSmark 2007 Preview is an application-based benchmark that reflects
usage patterns of business users in the areas of Video creation,
E-learning, 3D Modeling and Office Productivity.
The benchmark
utilities utilize real life applications like: Adobe After
Effects 7, Adobe Illustrator CS2, Adobe Photoshop CS2, AutoDesk 3ds Max
8, Macromedia Flash 8, Microsoft Excel 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003,
Microsoft PowerPoint 2003, Microsoft Word 2003, Microsoft Project 2003,
Microsoft Windows Media Encoder 9 series, Sony Vegas 7, SketchUp 5 and
WinZip 10.0.

Again, most applications that do not include 3D graphics will not be accelerated by the i7-920 processor, at least compared with a faster CPU in terms of GHz. Despite that, the i7-920 managed to get an overall rating pretty close to the one the Intel E8600 got.
5. Benchmarks - MAXON CINEBENCH, x264 HD Benchmark, TMPGEnc 4 Xpress
 MAXON CINEBENCH is based on MAXON's award-winning animation software, CINEMA 4D, which
is used by studios and production houses worldwide for 3D
content creation.
MAXON CINEBENCH is based on MAXON's award-winning animation software, CINEMA 4D, which
is used by studios and production houses worldwide for 3D
content creation.
MAXON CINEBENCH runs several tests on your computer to measure the
performance of the main processor and the graphics card under real
world circumstances. The benchmark application makes use of up to 16
CPUs or CPU cores and is available for Windows (32-bit and 64-Bit) and
Macintosh (PPC and Intel-based). The resulting values among different
operating systems are 100% comparable and therefore very useful with
regard to purchasing decision-making.

The CineBench R10 benchmark unveiled the power of the i7-920 CPU at least in the case where all the four cores were used. The processor was 26 % faster than the Intel Q9300.
- x264 HD Benchmark
x264 Benchmark utilizes the next generation of Video Encoding benchmarks with support
for x264 codec that is considered to be one of the most demanding for
Video applications. Simply put, it is a reproducible measure of fast your machine can encode a short, HD video clip to a high quality x264 video file. It's nice because everyone running it will use the identical video clip and software. The video encoder (x264.exe) reports a fairly accurate internal benchmark (frames per second) for each pass of the video encode and it also uses multi-core processors very efficiently. All these factors make this an ideal benchmark to compare different processors and systems to each other.
The benchmark procedure is very simple, you just run a batch file
that encodes the same file four times. The software provides two results, one for each pass of encoding. The average performance of this test is available in the charts below.

The x264 HD benchmark stresses out each cpu, since it uses the 100% of its resources. As it was expected, the Intel i7-920 is faster in both FPS1 and FPS2 tests. The CPU was 19% faster by the Intel Q9300 and 13% faster than the AMD 9950BE (first pass of encoding).
- TMPGEnc 4 Xpress
With MPEGEncoder, the overall encoding time will be reduced as CPU speed gets faster. TMPGEnc converts *.AVI files to MPEG1, the format which is used in VideoCDs. Using a variety of options in TMPGEnc, you can compress your video file in high quality. TMPGEnc enables you to adjust bit rate, quantize matrix, GOP structure, interlacing and many other parameters so that you can create the most appropriate movie file depending on your needs.
For our test we use an AVI file around 350MB encoded with the Xvid (Mpeg4 ASP) codec. We use the build-in Mpeg4 ASP/AVC MediaEncoder profile and by dividing the amount of total frames via the encoding time, we get the average frame/sec speed of each processor.

Again, the Intel i7-920 is more efficient in both ASP/AVC encoding. Compared with the Q9300, it is faster by almost 25FPS.
6. Benchmarks - SuperPI, wPrime
SuperPI has become a utility for benchmarking modern systems. In August 1995, the calculation of pi up to 4,294,960,000 decimal digits was succeeded by using a supercomputer and SuperPI, in the University of Tokyo. The program was written by D.Takahashi and he collaborated with Dr. Y.Kanada at the computer center, the University of Tokyo.

The software offers up to 32M calculations of PI numbers. For our tetsts, we selected 8M calculations:
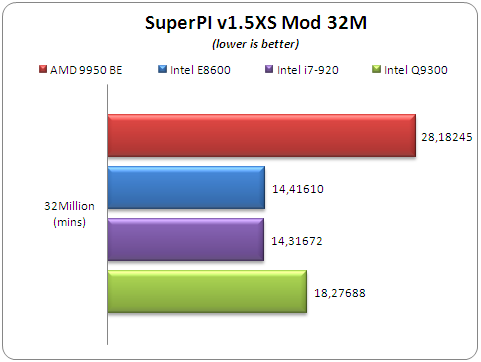
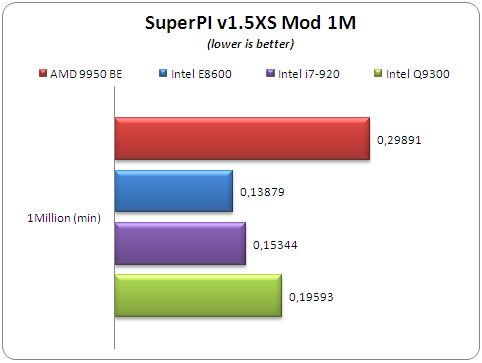
This time, the Intel i7-920 got a very low score..
- wPrime
wPrime is a benchmarking application designed to use a highly multithreaded approach to calculating the square-roots of large amounts of numbers (up to 32 billion at this stage!)
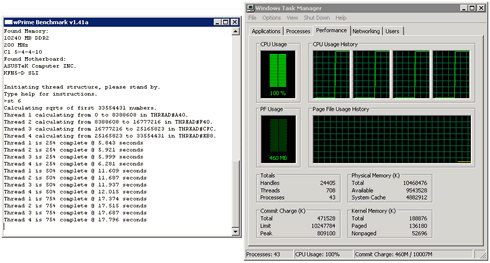
Theh software utilizes all the cores of a quad processor, therefore it can finish the fask much faster than a C2D.

7. Benchmarks - 3DMark06, Crysis v1.2
 3DMark®06 is the worldwide standard in advanced 3D game performance benchmarking. The software uses advanced real-time 3D game workloads to measure PC performance using a suite of DirectX 9 3D graphics tests, CPU tests, and 3D feature tests. 3DMark06 tests include all new HDR/SM3.0 graphics tests, SM2.0 graphics tests, AI and physics driven single and multiple cores or processor CPU tests and a collection of comprehensive feature tests to measure gaming performance.
3DMark®06 is the worldwide standard in advanced 3D game performance benchmarking. The software uses advanced real-time 3D game workloads to measure PC performance using a suite of DirectX 9 3D graphics tests, CPU tests, and 3D feature tests. 3DMark06 tests include all new HDR/SM3.0 graphics tests, SM2.0 graphics tests, AI and physics driven single and multiple cores or processor CPU tests and a collection of comprehensive feature tests to measure gaming performance.

The CPU test rely on AI, physics and game logic to generate a multi-threaded workload that can be distributed on multiple processors, cores or even on a single processor. Aegia PhysX library and D* Lite path finding AI algorithm are used to produce demanding CPU loads. It is obvious that the i7-920 CPU was pretty strong here and got the best score.
However, the overall 3D game performance was not significantly higher than the other CPUs of this test. Despite the numerous enhancements of the new i7-920 CPU, it seems that your expectations for higher FPS at games should ne limited.
We will find out more on that by running a Crysis (1024x768) CPU benchmark:

We cannot say that we have an absolute winner here. All CPUs performed almost equally, and the new i7-920 processor did not made the difference. The Intel E8600 did the same job. Considering that the E8600 is around 640MHz faster than the Intel i7-920 processor and that its cost is much lower than its new brother, we may say that the C2D processors is a better value-for-money solution. Of course, the i7-920 could be more futureproof as more games that use multiple cores are expected to appear.
8. Overclocking
Overclocking the new Intel i7 series is somehow different than you may have experienced until now since the Term "FSB" has now been replaced by four multipliers on the motherboard, which are used to change the system's speed:
-
CPU Speed: When multiplied by the system base clock speed (default 133.33 MHz) gives the CPU frequency. Four multipliers are used to define different speeds based on the number of active CPU cores.
-
Memory Speed: When multiplied by the system base clock speed gives the memory frequency. For example a memory multiplier of 10 times the base clock of 133.33 MHz results in a memory frequency of 1333 MHz.
-
Quick Path Interconnect (QPI) Speed: Selectable transfer rate of data transferred between the CPU and the IOH.
-
Uncore Speed: This multiplier applies to the non-CPU related items in the processor. The limit on this multiplier is set by the memory multiplier.
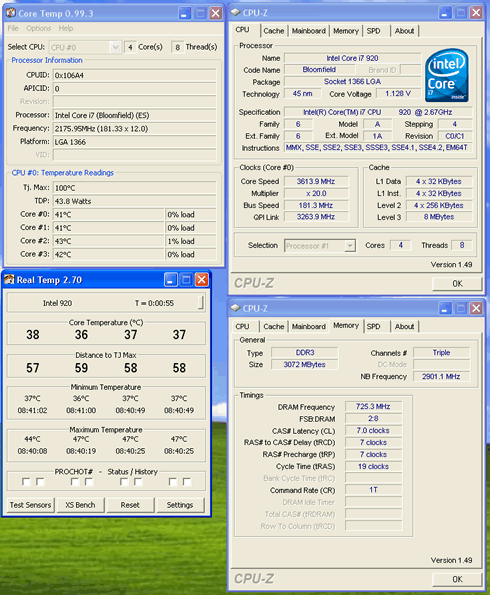
Since the Intel Core i7-920 is multiplier-locked, you can only increase the base clock (CPU Speed). For our tests we used the Intel stock cooler, which proved to be very efficient, at least for the short time overclocking (~30mins) period we used to test the system's stability. Using bigger and aftermarket coolers could further improve overclocking and increase your processor's life.
The default Vcore for the Intel Core i7-920 is 1.10V. You need to manually increase the Vcore - the sweet point for getting up to 3.60GHz (!) is the 1.25V. Since the memory is synced to the Bus speed, a good idea is to increase the DDR3 voltage as well, with the 1.65V to be the maximum value. Our first attempt was successful and very stable, even with the Intel's stock cooler installed. We also enabled the Turbo function, hence the Bus speed was reported at 181.3MHz, although we had set it at 180MHz through the BIOS.

Although the 1.25Voltage is considered as high, the reported temperatures were adequate. The CoreTemp software reported a temperature of ~75 degrees Celsius, while the RealTemp gave ~70 degrees at full load. Meanwhile, the memory was running at CL9 so we may be able to further tune this and get better results.

The temperature at idle mode, was ~ 40 degrees Celsius and this time, we had the memory running at CL7@ 1450MHz, while the Intel Core i7-920 was running at 3.60GHz.
If you want to get even higher, you should further increase the Vcore. The sweet point of the 3.80GHz should be stable enough with 1.35V. The Crucial memory had to be moved to CL8 since we had already reached the 1530MHz with 1.65V. At that time, the CPU temperature was very high (90 degrees C) with the Intel stock cooler installed. So it would be recommended to use a better cooler at these speeds.
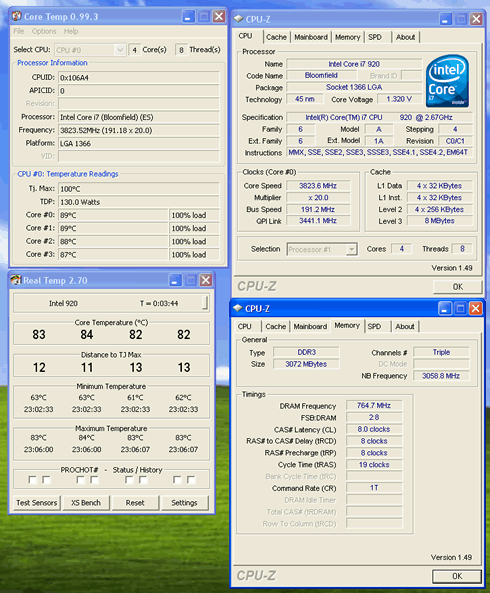
By using a water-cooling solution and a higher Vcore, it is possible to reach the 4.0GHz.
It would be interesting to see here where an Intel Core i7-920 stands against an overclocked Q9300 at their "maximum" speeds:
Benchmark |
Intel Q9300@3.52GHz |
Intel Core i7-920@3.60GHz |
% Difference (in favor of i7-920) |
x264 HD Benchmark |
43.51 |
61.46 |
+29.20% |
SuperPI |
4.08969 |
2.99376 |
+36.61% |
CineBench R10 |
15307 |
21324 |
+28.22% |
TMPGEnc 4 Xpress |
246.03 |
355.20 |
+30.73% |
wPrime |
13.656 |
7.781 |
+43.02% |
PCMark Vantage |
4910 |
4994 |
+1.68% |
3DMark 06 |
3527 |
3540 |
+0.37% |
The overclocked Intel Core i7-920 CPU gives an impressive performance, especially in the Video encoding applications. The performance difference is up to 28~36%, while at the wPrime reaches up to 43%! However, when looking at office applications over PCMark Vantage, the i7-920 is has a very small lead over the Intel Q300 CPU.
9. Conclusion
 The newly introduced Intel Core i7 series of CPUs pack several interesting technologies and the inclusion of the memory controller at the chipset further boosts memory performance. The Intel Core i7-920 is the lowest-priced product but still, its ~€290 retail price makes it quiet expensive for entry level users. In addition, the newly introduced socket LGA 1366 requires a new chipset to work with and all the currently available X58 motherboards are very expensive. Finally, in order to maximize the platform's performance you do need to invest on new triple-channel DDR3 memory. In short, in order to get a system running, you have to spend around €700+ and get at least a 30% higher performance than an Intel C2Q9300 processor.
The newly introduced Intel Core i7 series of CPUs pack several interesting technologies and the inclusion of the memory controller at the chipset further boosts memory performance. The Intel Core i7-920 is the lowest-priced product but still, its ~€290 retail price makes it quiet expensive for entry level users. In addition, the newly introduced socket LGA 1366 requires a new chipset to work with and all the currently available X58 motherboards are very expensive. Finally, in order to maximize the platform's performance you do need to invest on new triple-channel DDR3 memory. In short, in order to get a system running, you have to spend around €700+ and get at least a 30% higher performance than an Intel C2Q9300 processor.

The question might be who would be benefited from such an investment... There are many power users who always seek to get the latest and fastest systems and thus, they are willing to spend money for it. The X58 is a gaming platform that also supports both ATI's Crossfire and Nvidia's SLI technologies, simplifying future graphics setups.
However we feel that not many users are looking for such high-priced solutions, unless you cannot do without playing your games at resolutions of 1920+ ..
Getting down to the facts, the Intel Core i7-920 is much faster than any currently sold C2D/C2Q processor. The embedded memory controller does the job very well and as it was expected, the overclocking margins are very wide. We managed to overclock the CPU more than 1.0GHz higher than its nominal clock,

However, have in mind that such overclocking attempts require to install an aftermarket CPU cooling cooling since the produced heat is high, despite the 45nm manufacturing process.
Getting to the high-end Intel Core i7-965 requires a fortune but this processor is multiplier unlocked, so it might offer you much more space for overclocking.
We feel that gamers would be more benefited by an Intel E8500/8600 processor after overclocking, since not many games are currently taking full advantage of the new i7 CPUs. So at least for now, we think that the investment is weak. Prices are expected to decline in more than 6 months from now, according to industry sources. But with Intel already talking about a "new" LGA platform that will come some time in the middle of 2009, we feel that the i7 series will hardly power the mainstream PCs.