Cadence announced the Tensilica DNA 100 Processor IP for on-device AI, with up to four times the multiply-accumulate units and up to 12 times the performance of its Vision C5 launched last year.
The DNA 100 core supports sparsity in weights and activations and can prune neural networks to deliver higher levels of performance.
To date, high-end smartphones have led the way in adopting deep learning for inference jobs with handset SoC vendors. Designers are now working on AI acceleration in SoCs for surveillance cameras, smart speakers, cars, and AR/VR and IoT devices. The computational requirements (and the power and silicon budgets to pay for them) vary a lot depending on the end market. For example:
- IoT is less than 0.5 TMACS
- Mobile is 0.5 to 2 TMACS
- AR/VR is 1-4 TMACS
- Smart surveillance is 2-10 TMACS
- Autonomous vehicles from 10s to 100s of TMACS
Cadence clocked a 16-nm DNA 100 with 4,000 MACs at up to 2,550 frames/second and up to 3.4 TMACs/W on ResNet-50. A single 16-nm core running at 1 GHz can deliver up to 8 TMACs (12 TMACs using network pruning), and multiple cores can be embedded in an SoC to hit hundreds of TMACs.
The numbers would appear to beat Arm's first ML core that it said in May targets 4.6 tera-operations/second (TOPS) and 3 TOPS/W at 7 nm for high-end handsets.
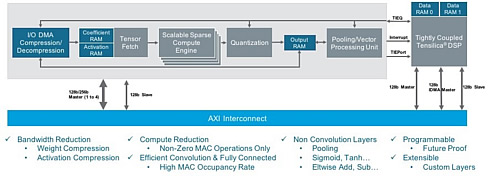
The DNA 100 processor architecture is shown in the block diagram above. The left-hand gray background block is a sparse compute engine with high MAC utilization. The block on the right is a tightly coupled Tensilica DSP that controls the flow of processing, and also future-proofs designs by providing programmability. You can think of these two blocks as the orchestra and the conductor.
The DNA 100 architecture is scalable internally, mostly by how many MACs are included. It can easily scale from 0.5 to 12 TMACS. The next level of scaling is to put several DNA 100 cores on the same chip, communicating via some sort of network-on-chip (NoC). If that is not enough, multiple chips (or boards) can be grouped into a huge system. Autonomous driving has been described as requiring a super-computer in the trunk. This is how you build a supercomputer like that.
The core supports 8-bit integer as well as 16-bit floating-point and integer formats. It runs graphs created with TensorFlow and Android neural-net frameworks. Cadence is developing support for Facebook's Glow compiler and associated PyTorch 1.0 framework and has on its roadmap plans to support Amazon's MxNet and other frameworks.
The DNA 100 core will be available in December with general availability before April.